100% Pass Ensure 2V0-642 Dumps with Free VCE and PDF (Question 161 – Question 180)
100% pass guarantee PassLeader 2V0-642 VCE and PDF dumps: https://www.passleader.com/2v0-642.html (245 Q&As –> 296 Q&As)
P.S. Free & New 2V0-642 dumps are available on Google Drive shared by PassLeader: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpbVl3X1hXbUdteHc
QUESTION 161
Which Virtual Machine cannot be protected by the Distributed Firewall?
A. A Virtual Machine connected to a vDS Portgroup running on an ESXi 5.1 host.
B. A Virtual Machine connected to a vSS Portgroup running on an ESXi 5.5 host.
C. A Virtual Machine connected to a vDS Portgroup running on an ESXi 5.5 host.
D. A Virtual Machine connected to a logical switch running on an ESXi 5.1 host.
Answer: D
QUESTION 162
Which statement is correct when upgrading vShield Data Security to NSX Data Security?
A. NSX Data Security does not support a direct upgrade.
B. NSX Controller must be deployed before the upgrade.
C. The vCloud Network and Security Virtual Wires must have been upgraded.
D. vCould Network and Security must be at least version 5.1 before starting the upgrade.
Answer: A
QUESTION 163
A new ESXi 5.5 host is deployed in a vSphere environment with VMware NSX for vSphere. How can the host be prepared for VMware NSX for vSphere?
A. By using Image Builder to pre-load the NSX for vSphere VIBs in the ESXi image in an Auto Deploy solution.
B. By leveraging VMware Update Manager to install the new NSX for vSphere VIBs into each of the hosts.
C. By creating a new VMkernel port in the host from the Host and Clusters inventory view in vSphere Web Client.
D. By entering the ESXi 5.5 management IP address in the NSX Controllers so the VIBs can be installed.
Answer: A
QUESTION 164
What is determined when an NSX Administrator creates a Segment ID Pool?
A. The range of VXLAN Network Identifiers (VNIs) that can be assigned to Logical Switches.
B. The total number of Logical Switches that can be deployed in a single Compute Cluster.
C. The range of VLAN segments that can be assigned to Transport Zones.
D. The total number of addresses that can be used to assign VTEP IP addresses to ESXi hosts during host preparation.
Answer: A
QUESTION 165
An administrator consults with the network team and decides that Transport Zones will be configured with Hybrid Replication Mode for a new NSX for vSphere deployment. Which statement is true?
A. The Ethernet segments where the VTEPs are connected have some level of multicast support.
B. The physical network is configured to support multicast.
C. The ESXi hosts in the Transport Zone are running on different server hardware.
D. A multicast range has been configured in the NSX Manager as part of the Logical Network Preparation.
Answer: A
QUESTION 166
An administrator has created an NSX network as shown in the exhibit.
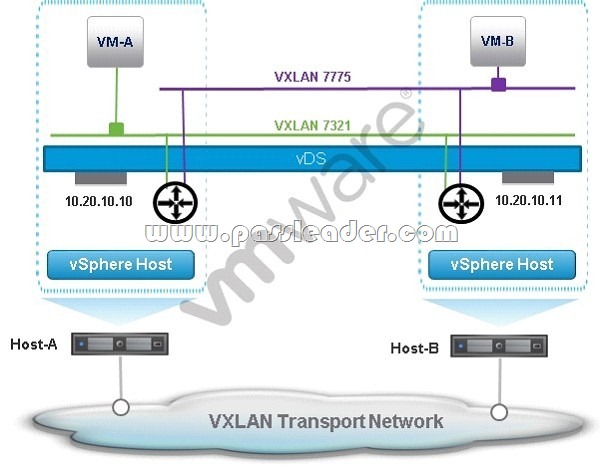
Both VMs in the exhibit use the same distributed router for their default gateway. VM-B obtains its IP address via DHCP. VM-A wants to send a packet to VM-B. How does VM-A learn VM-B’s MAC address?
A. If Host-A is made aware by the NSX Controller of VM-B’s MAC and IP addresses, Host- A replies directly to VM-A with an ARP response.
B. If Host-A is made aware by Host-B of VM-B’s MAC and IP addresses, Host-A replies directly to VM-A with an ARP response.
C. If the NSX Controller is made aware by Host-B of VM-B’s MAC and IP addresses, the NSX Controller replies directly to VM-A with an ARP response.
D. If Host-B is aware of VM-B’s MAC and IP addresses, Host-B is able to reply directly to VM-A with an ARP response.
Answer: A
QUESTION 167
An administrator has created the NSX network shown in the exhibit.
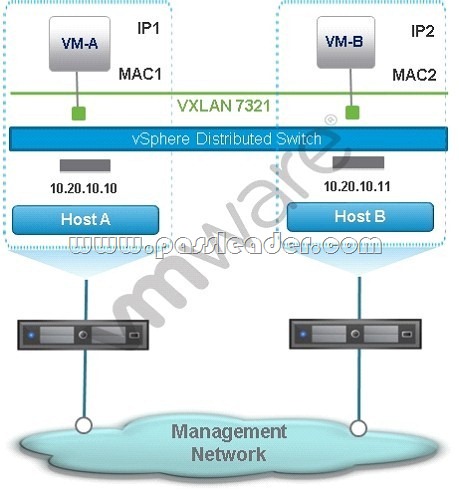
Both VMs use the same Distributed Router for their default gateway. VM-B receives an IP message from VM-A. What is the source MAC address of the IP message received by VM-B?
A. VM-A’s MAC address.
B. VM-B’s default gateway’s MAC Address.
C. VM-A’s default gateway’s MAC address.
D. Logical Switch 7321’s MAC address.
Answer: A
QUESTION 168
An NSX administrator creates the NSX network in the exhibit.
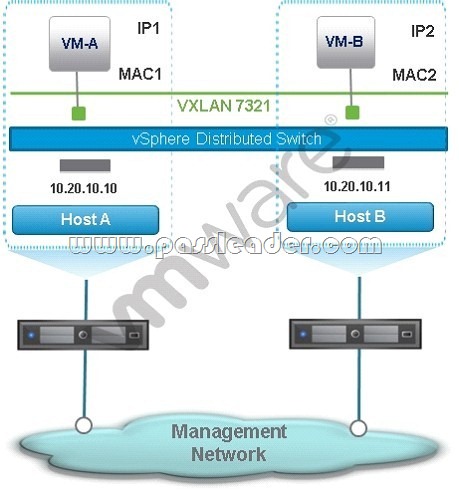
What destination IP address will Host-A use when sending a VXLAN frame to Host-B?
A. The IP address of one of Host-B’s new vmkernel ports created during host configuration.
B. The IP address of Host-B’s management vmkernel port, which is also the VTEP IP address.
C. The IP address of Host-B’s NSX Controller.
The NSX Controller forwards the VXLAN frame to Host-B.
D. The IP address Host-B provided to Host-A during VXLAN tunnel setup negotiations.
Answer: A
QUESTION 169
How is the Bridge Instance chosen?
A. It is chosen based on the ESXi host where the Logical Router Control VM is running.
B. It is manually assigned by the vSphere administrator when the distributed portgroup is configured.
C. During an election process among all ESXi hosts.
The host with the highest MAC address is selected.
D. The VTEP configured with the highest VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI) is selected.
Answer: A
QUESTION 170
Which two options are use cases of Layer 2 bridging in NSX for vSphere? (Choose two.)
A. Extend the network security to physical devices in the physical network by use of the Distributed Firewall.
B. Extend physical services to Virtual Machines in virtual network.
C. Allow clustering of multiple NSX Managers in a single vCenter Server instance.
D. Allow physical devices in the physical network to use the NSX Edge Gateway as a default router.
Answer: BD
QUESTION 171
Which components are required to enable layer 2 bridging? (Choose two.)
A. Distributed firewall rule to allow layer 2 traffic in the bridge.
B. Deployed Logical Switch.
C. Deployed Logical Router.
D. VLAN trunk configured on logical switch.
Answer: AC
QUESTION 172
Which two are valid types of authentication for an OSPF area? (Choose two.)
A. Password authentication
B. MD5 authentication
C. SHA1 authentication
D. LDAP authentication
Answer: AB
QUESTION 173
A vSphere administrator wants to add a VLAN LIF to a Distributed Router. What must the vSphere administrator do for the VLAN LIF to be added successfully?
A. The vSphere administrator must assign a VLAN number to the distributed portgroup that the VLAN LIF connects to.
B. The vSphere administrator must assign a VLAN number to the Distributed Router that the Logical Switch connects to.
C. The vSphere administrator must assign a VLAN number to the Logical Switch that the Distributed Router connects to.
D. The vSphere administrator must assign a VLAN number to the uplink on the distributed switch that the VLAN LIF connects to.
Answer: A
QUESTION 174
A vSphere administrator added a new interface to a Distributed Router with a subnet of 172.16.10.0/24 and wants to make this subnet reachable to the rest of the network. How can the vSphere administrator achieve this?
A. Enable OSPF on the Distributed Router.
Configure the uplink interface in the Backbone area and redistribute into OSPF the 172.16.10.0/24 subnet.
B. Enable OSPF in the Distributed Router.
Configure the uplink interface in the normal area and the new interface with the subnet 172.16.10.0/24 in a Backbone area.
C. Enable OSPF on the Distributed Router.
Configure the uplink interface in the Backbone area and redistribute from OSPF the 172.16.10.0/24 subnet.
D. Enable OSPF on the Distributed Router.
Configure the uplink interface in the Backbone area and the new interface with the subnet 172.16.10.0/24 in a normal area.
Answer: D
QUESTION 175
An administrator has configured an NSX network as shown.
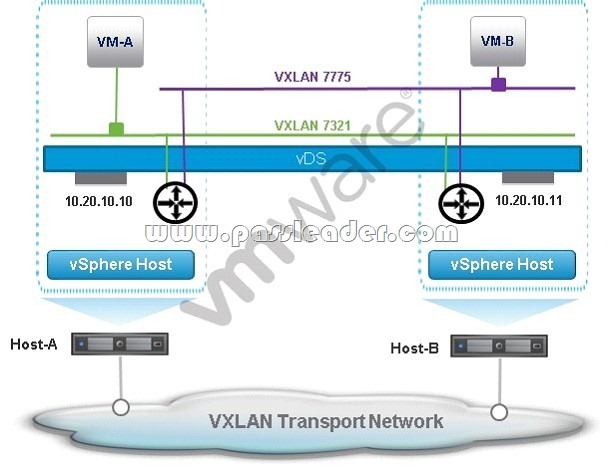
Both VM-A and VM-B use the same Distributed Router for their default gateway. If VM-A sends a packet to VM-B,what happens to the packet before it reaches VM-B?
A. Distributed Router in Host-A receives the packet from VM-A and forwards it to Logical Switch 7775 in Host-B, via a VXLAN frame, which delivers it to VM-B.
B. Logical Switch 7321 in Host-A receives the packet inside a frame from VM-A and forwards it to Logical Switch 7775 in Host-B, via a VXLAN frame, which delivers it to VM-B.
C. Distributed Router in Host-A receives the packet from VM-A and forwards it to Logical Switch 7321 in Host-B, via a VXLAN frame, which delivers it to Logical Switch 7775 before it is delivered to VM-B.
D. Logical Switch 7321 in Host-A receives the packet from VM-A and forwards it to the Distributed Router in Host-B, which passes it along to Logical Switch 7775 in Host-B before it is delivered to VM-B.
Answer: A
QUESTION 176
An administrator configures an NSX network as shown.

Both VM-A and VM-B use the same Distributed Router for their default gateway. VM-B receives an IP message from VM-A. What is the source MAC address of the IP message received by VM-B?
A. VM-B’s default gateway’s MAC address.
B. VM-A’s MAC address.
C. VM-A’s default gateway’s MAC address.
D. Logical Switch 7321’s MAC address.
Answer: A
QUESTION 177
Which two options are valid distribution methods used by the NSX Edge Load Balancer? (Choose two.)
A. Destination IP Hash
B. Least Load
C. URI
D. Round Robin
Answer: CD
QUESTION 178
A vSphere administrator deployed an NSX Edge Load Balancer in HA mode. What happens in the event the Load Balancer has a failure?
A. The secondary NSX Edge Load Balancer assumes the role of primary.
Existing Flows will need to have their connections reestablished.
B. HA will start the NSX Edge Load Balancer on another ESXi host in the cluster.
All existing flows will need to have their connections reestablished.
C. HA will start the NSX Edge Load Balancer on another ESXi host in the cluster.
The NSX Controller caches existing flows and hands them to the Load Balancer when it is back up.
D. The secondary NSX Edge Load Balancer assumes the role of primary.
The NSX Controller caches existing flows and hands them to the Load Balancer when it is back up.
Answer: A
QUESTION 179
A virtual machine, VM21, will be migrated between two ESXi 5.x hosts, labeled ESXi01 and ESXi02. Each host has two vSphere Standard Switches (vSS), configured as follows.
1. vSwitch0 has a portgroup labeled Management and a portgroup labeled vMotion.
2. The Management portgroup contains a vmkernel port tagged for management traffic.
3. The vMotion portgroup contains a vmkernel port tagged for vMotion traffic.
4. vSwitch0 on ESXi01 has a single uplink attached to the 10.1.20.0/24 network.
5. vSwitch0 on ESXi02 has a single uplink attached to the 10.1.20.0/24 network.
6. Each host has a vSwitch1 with a Production portgroup used by virtual machine traffic.
7. Each vSwitch1 has an uplink attached to the 10.1.40.0/24 network.
What is true about migrating VM21 to the new host?
A. vMotion would be supported in this configuration.
B. Storage vMotion would not be supported in this configuration.
C. vMotion would not be supported in this configuration.
D. Storage vMotion would be supported if the storage device supports VAAI.
Answer: A
QUESTION 180
A vNetwork Standard Switch has been configured for IP based load balancing uplinks. A new uplink is added to the switch. How will the additional uplink be configured by default?
A. The uplink is placed in standby mode until it is added to the active NIC team.
B. The uplink is considered active, but it will not participate in the active NIC team until assigned to a port group.
C. The uplink automatically becomes a part of the IP-based NIC team.
D. The uplink is marked as unused until it is added to the active NIC team.
Answer: C
100% valid 2V0-642 exam questions from PassLeader 2V0-642 dumps! Welcome to download the newest & 100% pass guarantee PassLeader 2V0-642 VCE and PDF dumps: https://www.passleader.com/2v0-642.html (245 Q&As –> 296 Q&As)
P.S. Free & New 2V0-642 dumps are available on Google Drive shared by PassLeader: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpbVl3X1hXbUdteHc